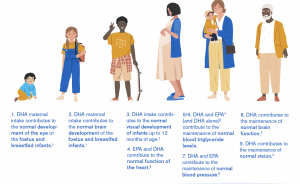
DHA is the most abundant fatty acid in the human brain.
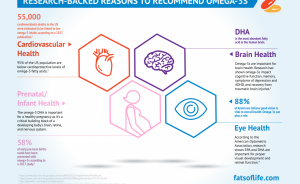
Omega-3s are important for brain health and function. At least 50% of the brain is fat. DHA is the most abundant omega-3 fatty acid in the brain and has been shown to have neuroprotective properties, while EPA has been linked to reducing inflammation. Research has shown an impact of omega-3s on cognitive function and memory, symptoms of depression, ADHD, and recovery from traumatic brain injuries.
Research shows that increased intake of omega-3s improves cognition and working memory, and may aid in slowing cognitive decline. Related to mental health, omega-3s play a role in mood regulation, helping the brain communicate using the neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine, and reducing inflammation in the brain which has been linked to depression.
Emerging science and clinical experience suggests that a high intake of EPA and DHA omega-3s may be beneficial for brain injury recovery including traumatic brain injury, concussion and post-concussion syndrome.
Emerging research also shows that omega-3s may aid in symptom management of ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder).
Read below about the many reasons to recommend omega-3s for your patient's brain.