Eicosapentaenoic acid & docosahexaenoic acid
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) are long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids that are abundant in fish, shellfish, some algae and genetically engineered plants. The body needs EPA and DHA to develop and function optimally in every stage of life.
There are more than 40,000 published studies on EPA and DHA, including more than 4000 human clinical trials. The vast body of science associated with omega-3s supports consumption for overall wellness, as well as specific cardiovascular and cognitive outcomes, dry eye syndrome, vision and brain development in infants and prevention of pre-term birth.
Recommended intakes supported by governments and scientific bodies around the world are to consume 500 mg of EPA and DHA per day for overall health, and higher quantities for specific life stages or health conditions. A 2016 study looking at the Omega-3 Index, which is the combined percentage of the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA in red blood cell membranes, in adults around the world showed that most of the global population – around 80% – consumes significantly less EPA and DHA than recommended.
Know Your Levels
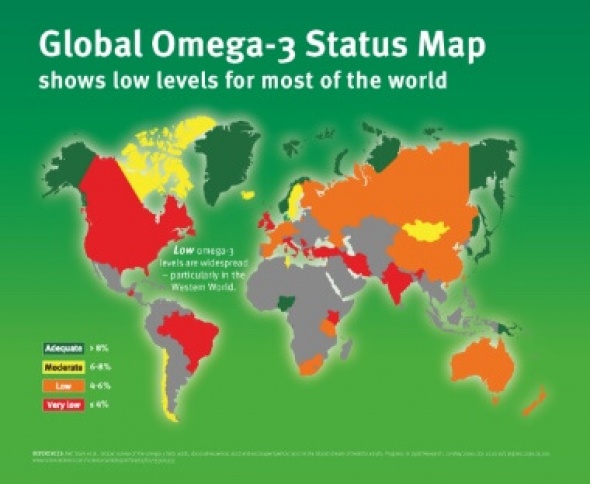
Knowing your omega-3 levels is important.
Measuring blood levels of EPA and DHA omega-3s is an easy way to assess how well a person’s diet is contributing to omega-3 status and whether interventions such as supplementation are needed. All that is required is a simple skin prick, which can be done in a doctor’s office or even at home. The blood sample is mailed to a lab, and results are emailed within 1-2 weeks. Learn more at OmegaQuant.com.

